Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of South Carolina: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of South Carolina: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of South Carolina: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of South Carolina: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines

South Carolina, known for its coastal charm and rich history, also harbors a less visible aspect: a network of geological fault lines that shape the state’s landscape and influence its seismic activity. Understanding these fault lines is crucial for comprehending the state’s vulnerability to earthquakes, informing preparedness measures, and guiding responsible development practices.
This article delves into the intricate world of South Carolina’s fault lines, providing a comprehensive overview of their location, characteristics, and significance. By examining the available data and research, we aim to shed light on the seismic potential of the state, highlighting the importance of ongoing monitoring and preparedness efforts.
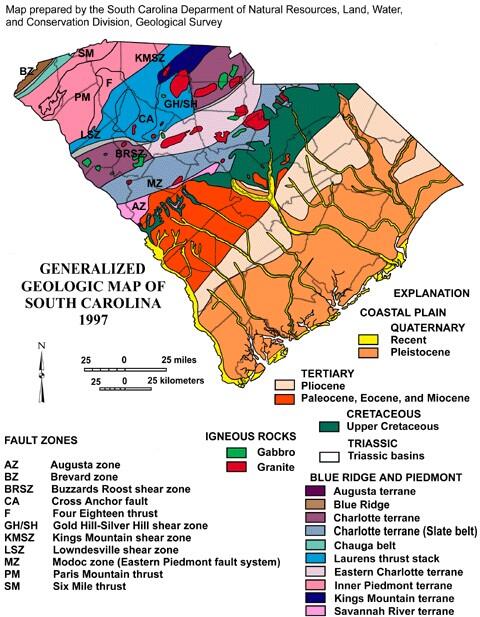
Mapping the Fault Lines: A Glimpse into South Carolina’s Geologic Past
South Carolina’s fault lines are remnants of a dynamic geological history, stretching back millions of years. The state’s complex geological framework is shaped by the interaction of tectonic plates, volcanic activity, and erosion. These processes have left their mark in the form of numerous faults, which represent fractures in the Earth’s crust where rock masses have moved relative to each other.
The Coastal Plain Fault System: A Dominant Feature
A prominent geological feature in South Carolina is the Coastal Plain Fault System. This extensive network of faults runs parallel to the Atlantic coast, extending from Virginia to Florida. The system is characterized by numerous faults, including the:
- Charleston-Summerville Fault Zone: Located in the southeastern part of the state, this fault zone is known for its potential to generate moderate earthquakes.
- Wateree River Fault Zone: This zone extends northwestward from the Charleston-Summerville Fault Zone, traversing the central part of South Carolina.
- Santee River Fault Zone: Located in the eastern part of the state, this fault zone is associated with significant geological deformation.
The Piedmont Fault System: A Hidden Network
In contrast to the Coastal Plain Fault System, the Piedmont Fault System lies beneath the state’s Piedmont region, often concealed beneath layers of sediment and rock. This system is characterized by a complex network of faults, including the:
- Brevard Fault Zone: A major fault zone that marks the boundary between the Blue Ridge and Piedmont provinces.
- Kings Mountain Fault Zone: This zone runs through the northwestern part of the state, extending into North Carolina.
The Appalachian Fault System: A Remote Influence
The Appalachian Fault System, located further west in the Appalachian Mountains, exerts a subtle influence on South Carolina’s geology. While not directly within the state’s borders, this system’s tectonic activity can trigger seismic events that are felt in South Carolina.
The Seismic Landscape: A Symphony of Tremors
South Carolina is not immune to earthquakes, though the state’s seismic activity is generally considered moderate compared to regions like California. Historical records and modern monitoring data reveal a pattern of small to moderate earthquakes occurring throughout the state.
The Charleston Earthquake of 1886: A Historic Reminder
One of the most significant seismic events in South Carolina’s history was the Charleston earthquake of 1886. This magnitude 7.3 earthquake caused widespread damage and fatalities, highlighting the potential for significant seismic events in the region.
Modern Monitoring: Unveiling the Seismic Pulse
To better understand South Carolina’s seismic activity, scientists rely on a network of seismographs strategically placed across the state. These instruments detect and record ground vibrations, providing valuable data on earthquake frequency, magnitude, and location. This information is crucial for assessing seismic hazards and informing preparedness efforts.
Understanding the Risks: A Foundation for Resilience
While South Carolina’s seismic activity is generally moderate, understanding the potential risks associated with its fault lines is crucial for ensuring public safety and promoting responsible development.
Seismic Hazards: A Multifaceted Threat
The presence of active fault lines in South Carolina poses several potential hazards, including:
- Earthquakes: The most direct hazard associated with fault lines, earthquakes can cause ground shaking, damage to infrastructure, and potential tsunamis in coastal areas.
- Landslides: Fault activity can destabilize slopes, leading to landslides that can damage property and threaten lives.
- Ground Subsidence: The movement of fault lines can cause the ground to sink, leading to damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Mitigation Strategies: Building Resilience
Recognizing the potential risks associated with South Carolina’s fault lines, various mitigation strategies can be implemented to enhance resilience and minimize the impact of seismic events. These include:
- Building Codes: Implementing robust building codes that incorporate earthquake-resistant design principles can significantly reduce the risk of structural damage.
- Seismic Retrofitting: Retrofitting existing buildings to meet current seismic standards can enhance their resilience to earthquakes.
- Emergency Preparedness: Developing comprehensive emergency plans that address potential earthquake scenarios is crucial for ensuring public safety and effective response.
- Public Education: Raising awareness about seismic hazards and promoting preparedness measures among the public is essential for fostering a culture of resilience.
FAQs about South Carolina’s Fault Lines
1. How often do earthquakes occur in South Carolina?
South Carolina experiences a moderate level of seismic activity, with small to moderate earthquakes occurring relatively frequently. While most earthquakes are too small to be felt, larger events can cause noticeable shaking.
2. Are there any areas in South Carolina more prone to earthquakes than others?
The Charleston-Summerville Fault Zone is considered the most seismically active region in South Carolina, with a higher likelihood of experiencing moderate earthquakes.
3. Can earthquakes in other parts of the world affect South Carolina?
While South Carolina is not directly impacted by earthquakes in distant regions, large-magnitude events can trigger minor seismic waves that are detectable in the state.
4. Is South Carolina at risk of a major earthquake like the one that struck California in 1906?
While a major earthquake similar to the 1906 San Francisco earthquake is possible, it is considered less likely in South Carolina due to the state’s overall lower seismic activity.
5. What can I do to prepare for an earthquake in South Carolina?
- Secure heavy objects that could fall during shaking.
- Develop a family emergency plan and practice earthquake drills.
- Learn how to shut off gas, water, and electricity in case of damage.
- Have a supply kit with essential items such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
Tips for Understanding South Carolina’s Fault Lines
- Explore Interactive Maps: Utilize online maps and resources that depict fault lines and seismic activity in South Carolina.
- Consult Local Resources: Contact local geological surveys and emergency management agencies for specific information on seismic hazards in your area.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to alerts and notifications from reliable sources to receive updates on seismic activity in South Carolina.
Conclusion: Embracing the Seismic Reality of South Carolina
The presence of fault lines in South Carolina serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust and the potential for seismic activity. Understanding the state’s geological framework and the risks associated with its fault lines is crucial for promoting public safety, responsible development, and a culture of preparedness. By embracing the seismic reality of South Carolina, we can build a more resilient and informed community, capable of navigating the challenges posed by this natural phenomenon.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of South Carolina: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!