Navigating the Canadian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions
Related Articles: Navigating the Canadian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Canadian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Canadian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions
/1481740_final_v31-439d6a7c421f4421ae697892f3978678.png)
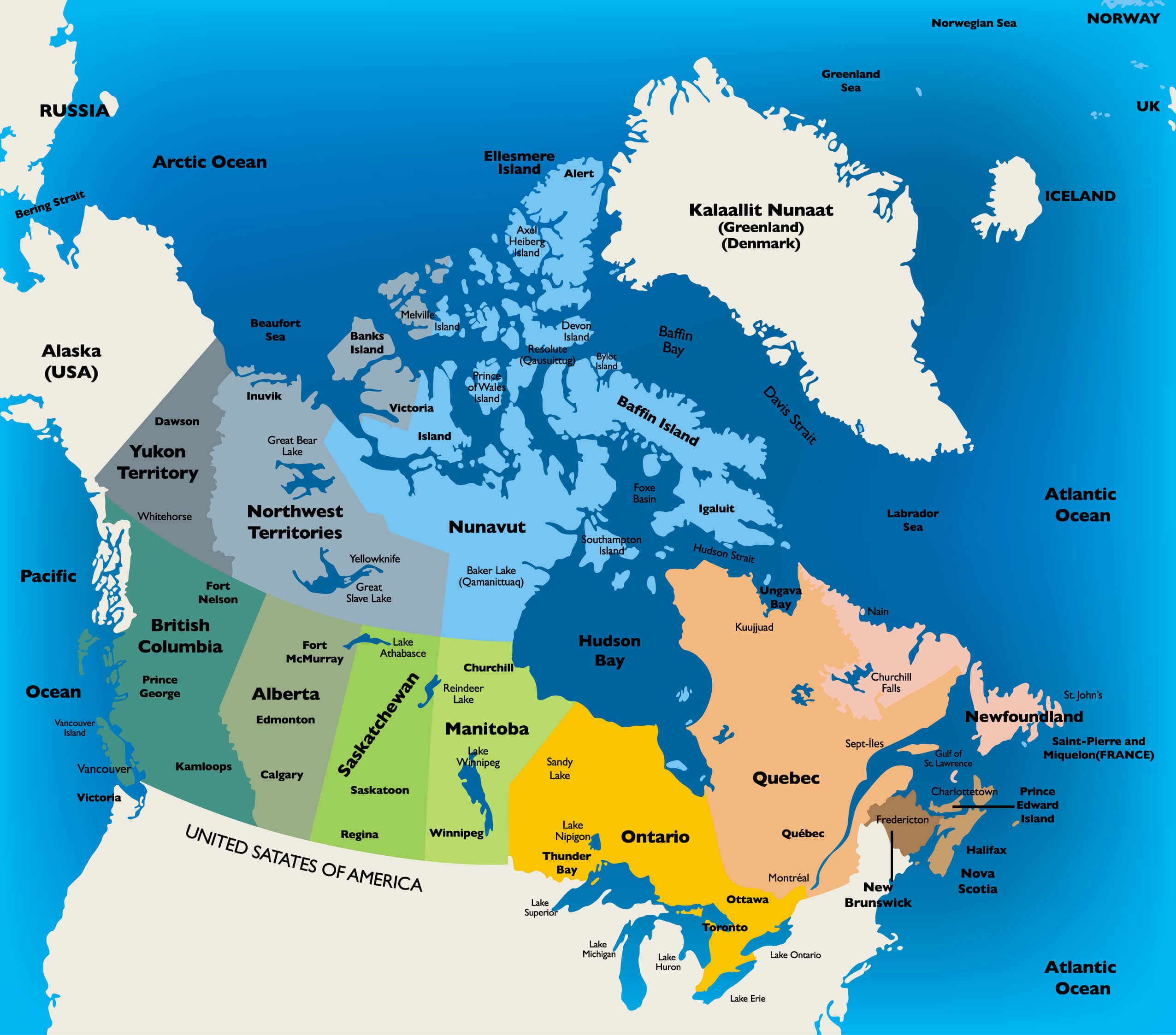
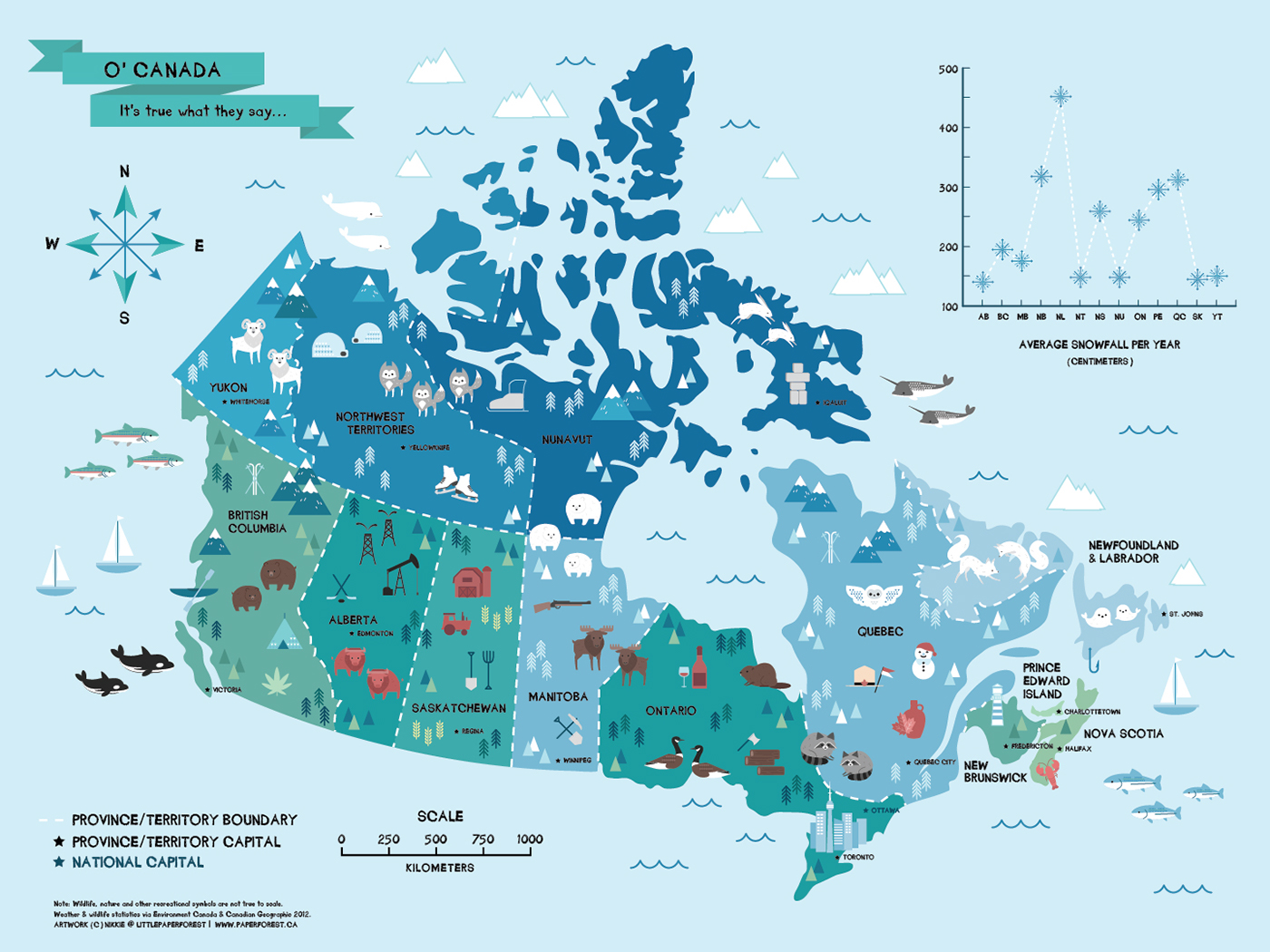
Canada, a vast and diverse nation stretching from the Atlantic to the Pacific, is often understood through its distinct regions. These regions, defined by a combination of geographic, cultural, and historical factors, offer a unique lens through which to appreciate the country’s multifaceted character. Understanding these regional divisions provides a valuable framework for comprehending Canadian identity, its economic landscape, and the diverse experiences of its people.
A Mosaic of Regions:
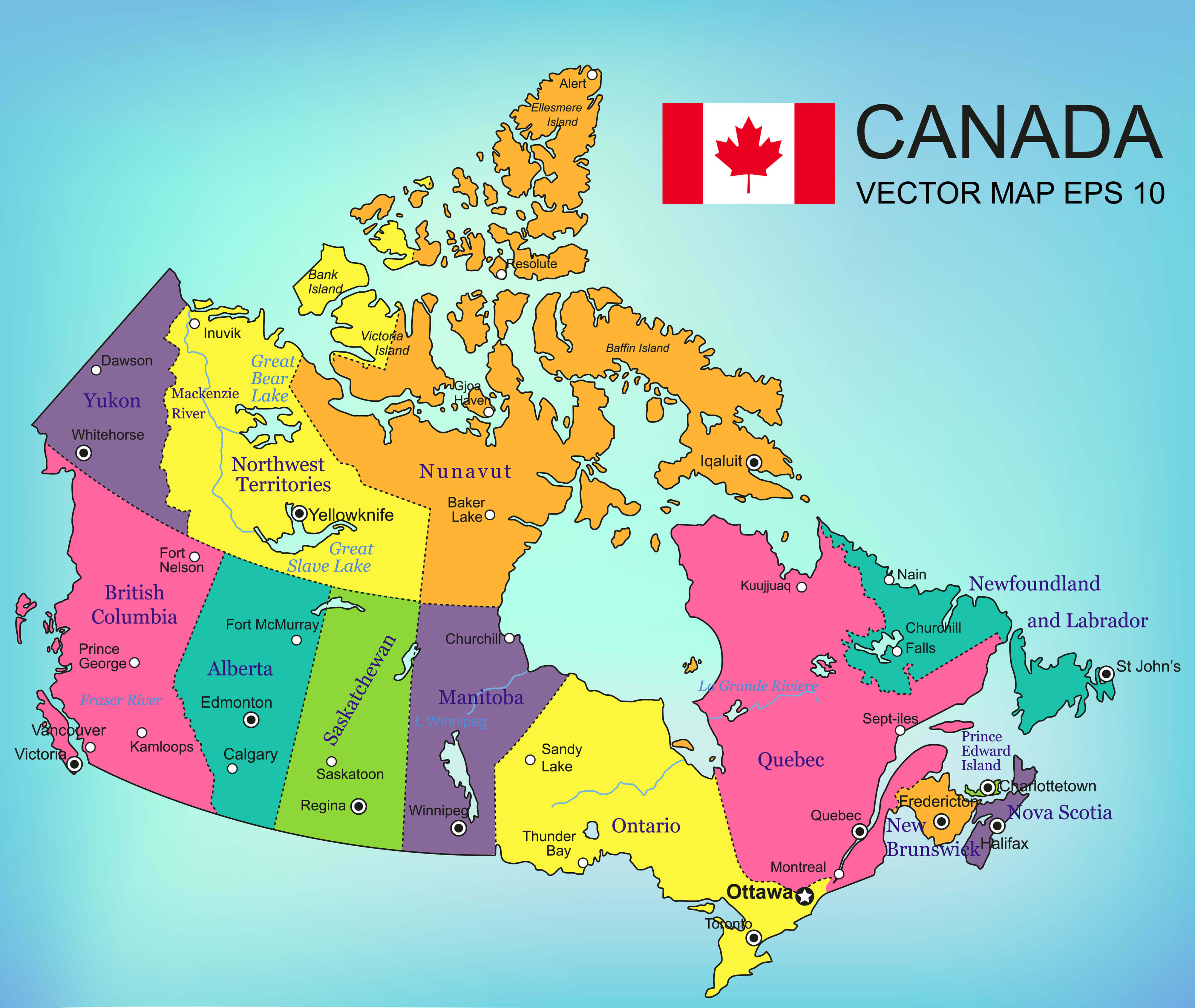
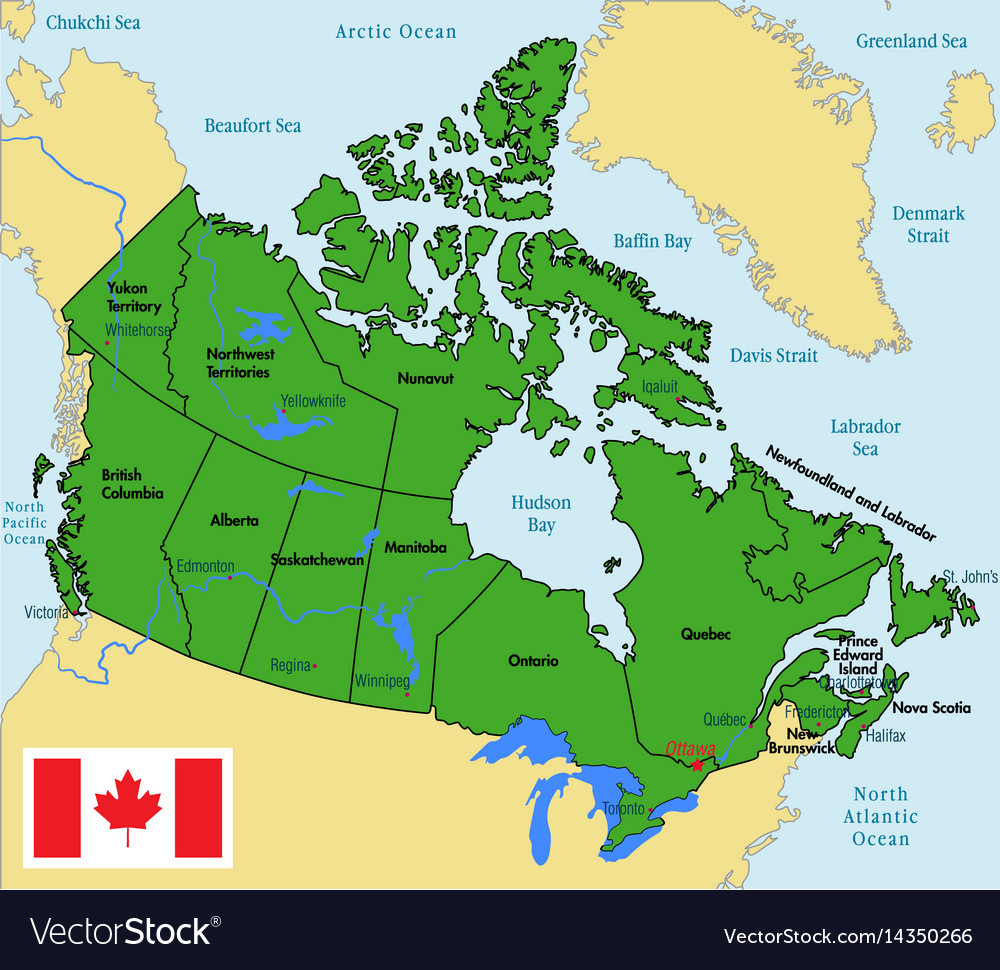
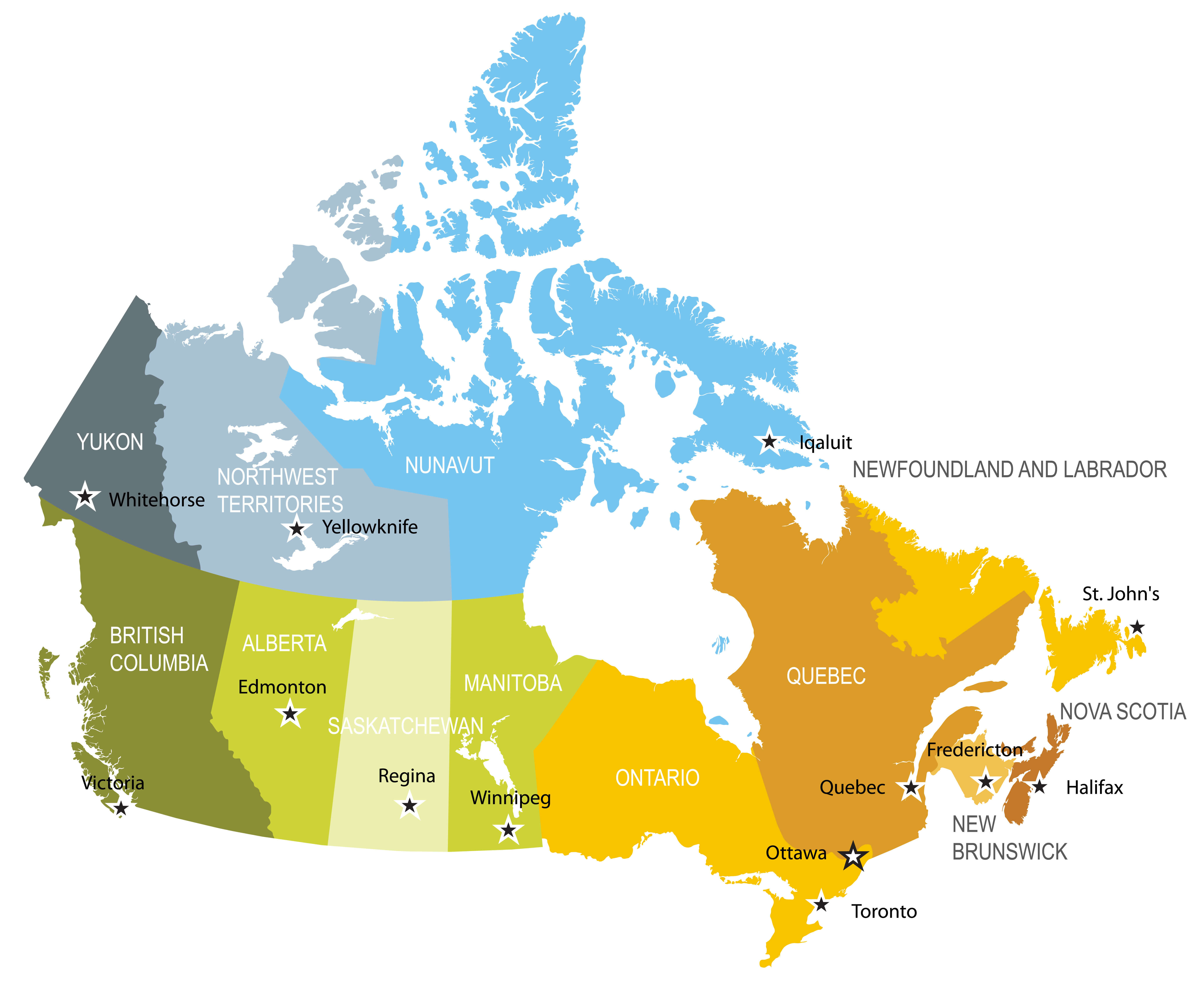
The traditional division of Canada into ten distinct regions is widely recognized, offering a convenient framework for understanding the country’s geography, cultural tapestry, and economic drivers. These regions are:
- Atlantic Canada: Encompassing the provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador, this region boasts a rich maritime history, stunning coastal scenery, and a vibrant cultural scene. Its economy is heavily reliant on fishing, forestry, and tourism.
- Quebec: The province of Quebec, with its unique French heritage and cultural identity, is a significant economic force in Canada. Its diverse industries include manufacturing, technology, and hydroelectricity, while its vibrant cultural scene attracts visitors from across the globe.
- Ontario: The most populous province in Canada, Ontario is a powerhouse of economic activity, boasting diverse industries including manufacturing, finance, and technology. The province is home to the nation’s capital, Ottawa, and the bustling metropolis of Toronto, making it a cultural and economic hub.
- Prairie Provinces: Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, collectively known as the Prairie Provinces, are characterized by their vast grasslands, agricultural dominance, and significant energy resources. The region’s economy relies heavily on agriculture, oil and gas extraction, and resource-based industries.
- British Columbia: Situated on the Pacific coast, British Columbia is renowned for its stunning natural beauty, including towering mountains, lush forests, and a rugged coastline. Its economy is driven by forestry, mining, tourism, and a burgeoning technology sector.
- Yukon: This vast territory in Canada’s north is known for its breathtaking wilderness, including majestic mountains, pristine lakes, and vast expanses of untouched land. Its economy relies heavily on tourism, mining, and resource extraction.
- Northwest Territories: Another vast territory in Canada’s north, the Northwest Territories is home to a diverse landscape, including boreal forests, arctic tundra, and numerous lakes. Its economy is driven by mining, resource extraction, and tourism.
- Nunavut: The largest and most sparsely populated territory in Canada, Nunavut is located in the Arctic and is home to a rich Inuit culture. Its economy is heavily reliant on hunting, fishing, and resource extraction.
- Northern Territories: This collective term encompasses the Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut, highlighting their shared geographical location, unique challenges, and cultural traditions.
- Canada’s North: This broader term encompasses the vast and sparsely populated regions of Canada north of the 60th parallel, including the Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, and northern parts of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba.
Beyond Traditional Divisions:
While the traditional ten-region model provides a useful framework, it’s important to acknowledge that Canada’s regional landscape is far more complex and nuanced. Other significant regional divisions are often considered, including:
- The Canadian Shield: This vast geological formation, covering much of central and eastern Canada, is characterized by rocky terrain, abundant lakes, and rich mineral deposits. It encompasses parts of Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, Nunavut, and the Northwest Territories.
- The St. Lawrence Lowlands: This fertile region along the St. Lawrence River is a major agricultural hub and home to some of Canada’s largest cities, including Montreal and Quebec City.
- The Great Lakes Region: This area encompasses the Great Lakes and surrounding regions, including parts of Ontario, Quebec, and the United States. It is a vital industrial and agricultural region, with a strong presence in manufacturing, shipping, and tourism.
- The Prairies: This vast grassland region, encompassing the Prairie Provinces, is a major agricultural producer, known for its wheat production and cattle ranching.
- The Canadian West: This broader term encompasses the provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia, highlighting their shared geographical location, economic ties, and distinct cultural influences.
The Significance of Regional Divisions:
Understanding the regional divisions of Canada is crucial for several reasons:
- Policy Development: Recognizing the unique characteristics and needs of different regions is essential for effective policy development. This includes addressing regional disparities in economic development, healthcare access, education, and infrastructure.
- Economic Analysis: Regional divisions provide a framework for analyzing economic trends, identifying growth opportunities, and understanding the impact of national policies on different parts of the country.
- Cultural Understanding: Regional divisions offer a lens through which to appreciate the diverse cultural tapestry of Canada. From the unique traditions of the Atlantic provinces to the vibrant multiculturalism of Toronto, each region boasts a distinct cultural identity.
- Environmental Management: Understanding regional differences in climate, terrain, and natural resources is essential for effective environmental management and conservation efforts.
- Tourism and Recreation: Regional divisions provide a framework for exploring the diverse landscapes and cultural experiences that Canada offers. From the rugged beauty of the Canadian Shield to the vibrant urban centers of the east coast, each region offers unique attractions for visitors.
FAQs about Map of Canadian Regions:
Q: How are Canadian regions defined?
A: Canadian regions are defined by a combination of geographical, cultural, historical, and economic factors. These factors include natural boundaries, dominant industries, cultural traditions, and historical development.
Q: What are the main differences between Canadian regions?
A: Canadian regions differ significantly in terms of their climate, geography, culture, economy, and population density. For example, the Atlantic provinces are known for their maritime history and coastal scenery, while the Prairie Provinces are characterized by their vast grasslands and agricultural dominance.
Q: Why is it important to understand Canadian regional divisions?
A: Understanding Canadian regional divisions is crucial for developing effective policies, analyzing economic trends, appreciating cultural diversity, managing environmental resources, and promoting tourism.
Q: Are there any other regional divisions in Canada besides the ten traditional regions?
A: Yes, there are other significant regional divisions in Canada, such as the Canadian Shield, the St. Lawrence Lowlands, the Great Lakes Region, and the Canadian West.
Q: How can I learn more about Canadian regional divisions?
A: You can learn more about Canadian regional divisions by consulting maps, reading books and articles, visiting museums, and engaging with local communities.
Tips for Navigating Canadian Regional Divisions:
- Explore Maps: Utilize online maps or physical atlases to visualize the different regions of Canada and understand their geographical relationships.
- Read Regional Literature: Seek out books, articles, and documentaries that focus on specific regions of Canada to gain insights into their history, culture, and economy.
- Engage with Local Communities: Connect with people from different regions of Canada to learn firsthand about their experiences and perspectives.
- Travel and Explore: Embrace the opportunity to travel to different regions of Canada to experience their unique landscapes, cultures, and attractions.
Conclusion:
The regional divisions of Canada provide a valuable framework for understanding the country’s diverse geography, cultural tapestry, and economic landscape. By recognizing the unique characteristics and challenges of each region, Canadians can foster a deeper understanding of their nation’s identity and work towards a more equitable and prosperous future. Understanding these regional divisions allows for a more nuanced appreciation of Canada’s complex and fascinating landscape, fostering a deeper understanding of its diverse people and the unique challenges and opportunities each region faces.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Canadian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Regional Divisions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!