Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Scale Bar
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Scale Bar
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Scale Bar. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Scale Bar

Maps are powerful tools, capable of shrinking vast landscapes onto manageable paper or digital screens. But without a clear understanding of the relationship between the map and the real world, their information remains inaccessible. This is where the scale bar steps in, acting as a crucial translator between the two realms.
A scale bar, often found on maps, is a graphic representation of distance. It visually demonstrates the relationship between the map’s depiction and the actual ground distance, allowing users to accurately measure and interpret distances on the map.
The Essence of Scale Bars
Imagine a map of a city, where a single line represents a street. This line is a scaled-down version of the actual street, but how do you determine the real-world length of that street? Here, the scale bar plays a crucial role. It provides a reference point, showing how much distance on the map corresponds to a specific distance on the ground.
For instance, a scale bar might indicate that one centimeter on the map represents one kilometer in reality. This means that every centimeter measured along a street on the map corresponds to one kilometer in the actual city.
Types of Scale Bars
Scale bars can be presented in various formats, each serving specific purposes:
-
Linear Scale Bar: This is the most common type, presenting a straight line divided into segments. Each segment represents a specific distance, allowing for direct measurement using a ruler. For example, a scale bar with markings for 1 kilometer, 2 kilometers, and 3 kilometers would enable users to measure distances on the map using a ruler.
-
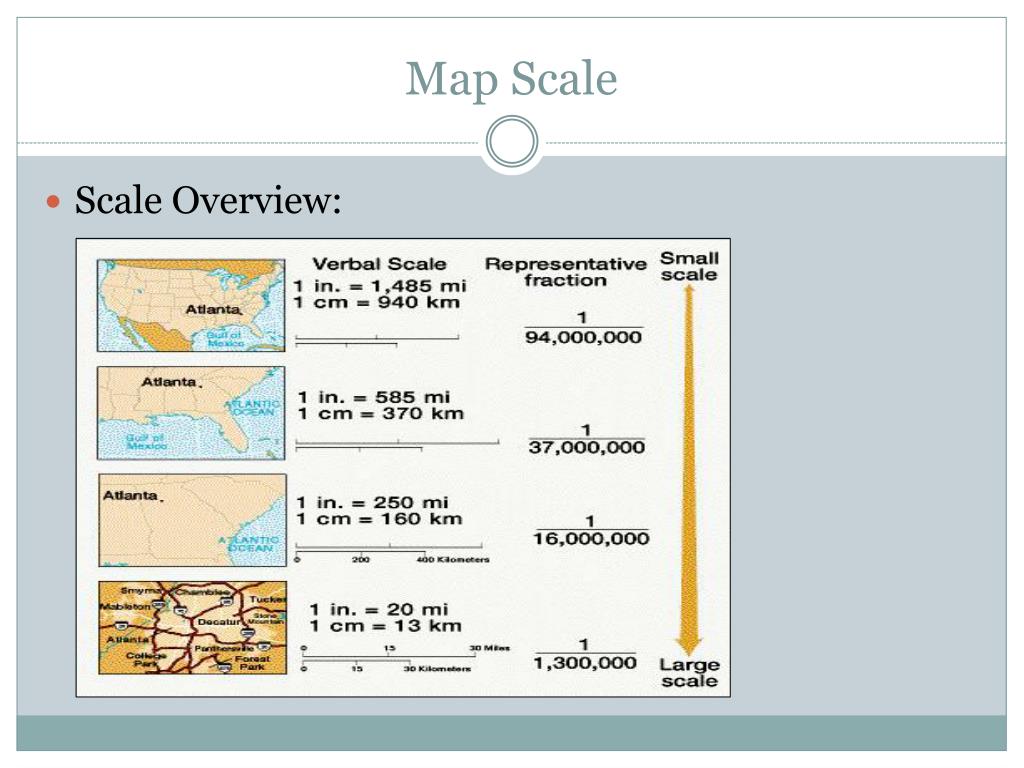
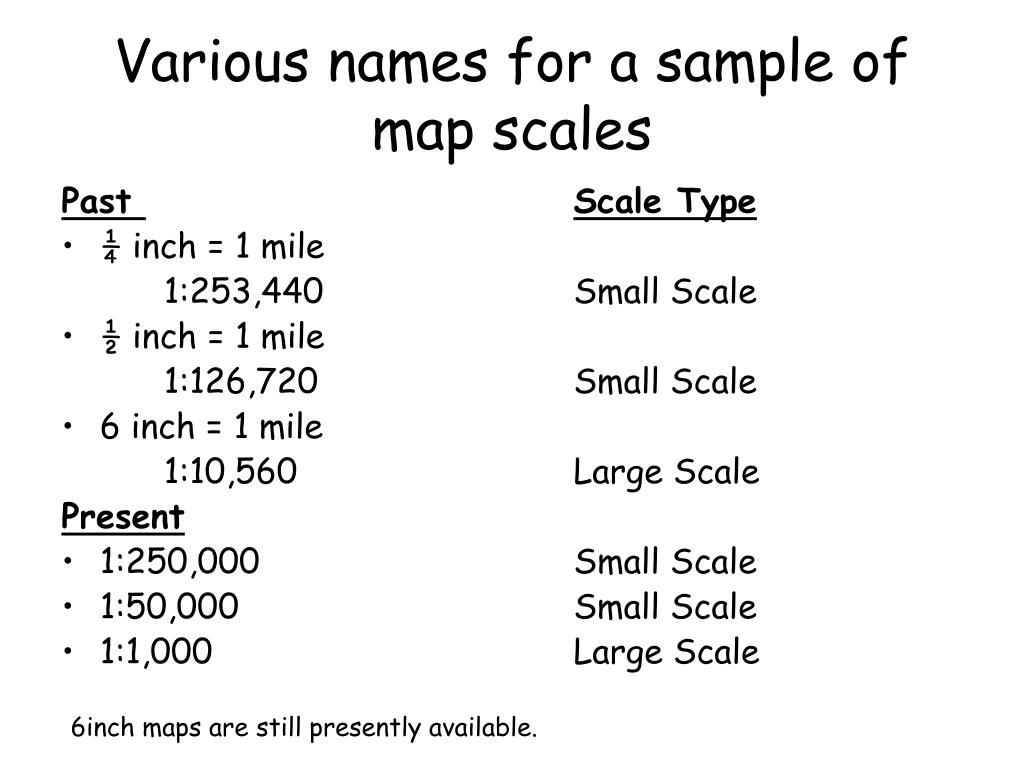
Verbal Scale: This scale is presented as a written statement, expressing the ratio between the map distance and the real-world distance. Examples include "1:100,000" or "1 cm = 1 km." This type is commonly used in conjunction with other scale representations.
-
Representative Fraction (RF) Scale: This scale is expressed as a fraction, representing the ratio between the map distance and the real-world distance. For example, an RF scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in reality. This format is particularly useful for calculations and comparisons across different maps.
The Importance of Scale Bars
The scale bar is an indispensable component of maps for several reasons:
-
Accurate Distance Measurement: The scale bar allows users to directly measure distances on the map and accurately translate them to real-world distances. This is crucial for various tasks, including planning routes, calculating travel times, and understanding the spatial relationships between different locations.
-
Map Interpretation: The scale bar provides a crucial reference point for understanding the map’s scale and interpreting its information. It helps users grasp the relative sizes and distances of features depicted on the map, facilitating spatial awareness and understanding.
-
Consistency and Standardization: Scale bars ensure consistency across different maps, enabling users to compare and analyze data from various sources. This standardization facilitates a uniform understanding of distances and proportions, regardless of the map’s origin or purpose.
-
Accessibility: Scale bars provide a visual and intuitive way to understand map scale, even for users unfamiliar with complex map notations or mathematical ratios. This accessibility enhances the usability and comprehensiveness of maps for a wider audience.
FAQs about Scale Bars
Q: Why is it important to use a scale bar when interpreting a map?
A: A scale bar provides a clear and direct reference for understanding the relationship between distances on the map and distances in the real world. Without a scale bar, it is impossible to accurately interpret distances and make informed decisions based on the map’s information.
Q: Can different maps use the same scale bar?
A: While different maps can use the same scale bar, it is not always necessary. The scale bar should be chosen based on the map’s purpose and the level of detail required. For example, a map of a city might have a different scale bar than a map of a continent.
Q: How do I use a scale bar to measure distances on a map?
A: You can use a ruler to measure the distance between two points on the map. Then, refer to the scale bar to determine the corresponding real-world distance. For example, if the distance between two points on the map is 5 cm and the scale bar indicates that 1 cm represents 1 km, then the real-world distance is 5 km.
Q: Are there any limitations to using a scale bar?
A: While scale bars are powerful tools, they are not without limitations. The accuracy of the scale bar is dependent on the map’s projection and the level of detail provided. Additionally, the scale bar may not be accurate for maps that have been distorted by factors like stretching or shrinking.
Tips for Using Scale Bars
-
Check the Scale Bar: Always check the scale bar before using the map to ensure you understand the relationship between the map distance and the real-world distance.
-
Use a Ruler: Use a ruler to accurately measure distances on the map, ensuring consistency and precision in your measurements.
-
Consider the Map’s Projection: Be aware of the map’s projection, as it can affect the accuracy of the scale bar.
-
Compare Different Scale Bars: If multiple scale bars are present on the map, compare them to ensure consistency and avoid potential errors.
-
Consult the Map’s Legend: The map’s legend may provide additional information about the scale bar and its usage.
Conclusion
The scale bar is a fundamental element of maps, acting as a bridge between the map’s representation and the real world. It provides a clear and concise way to measure distances, interpret map information, and ensure consistency across different maps. By understanding the role of scale bars and their various formats, users can effectively navigate and interpret maps, enhancing their understanding of the world around them.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Scale Bar. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!