A Geographic Overview of Iran and Its Neighbors
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Iran and Its Neighbors
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Iran and Its Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Iran and Its Neighbors
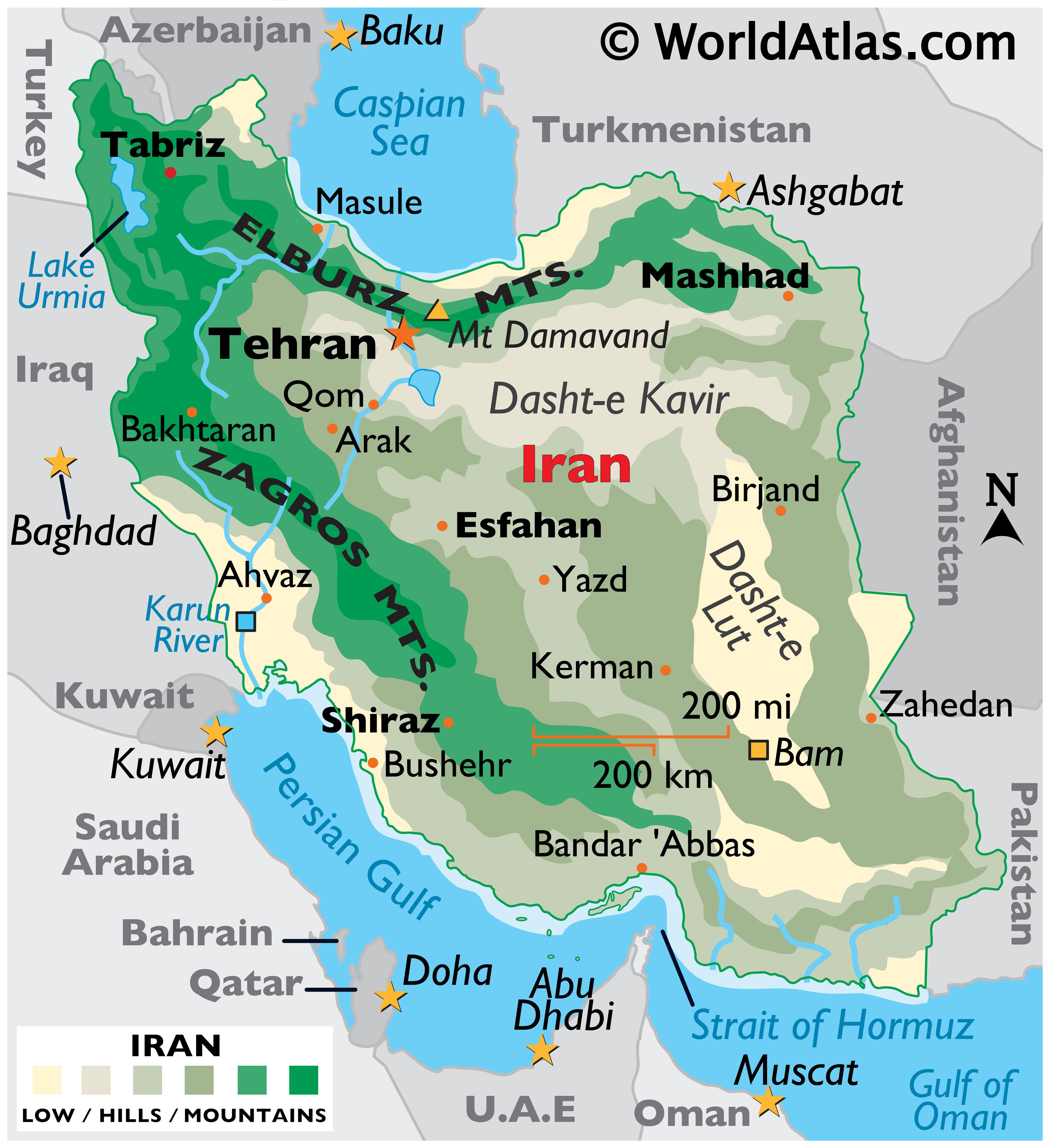
Iran, a nation steeped in history and culture, occupies a pivotal position in the heart of Eurasia. Its strategic location, nestled between the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Indian Ocean, has shaped its history, its economy, and its relationships with neighboring countries. Understanding the geography of Iran and its surrounding nations is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the region, its geopolitical significance, and the diverse cultures that call it home.
Iran: A Land of Contrasts
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, boasts a vast and diverse landscape. Its mountainous terrain, dominated by the Zagros and Alborz ranges, creates a striking contrast with its expansive deserts and fertile plains. The country’s geographical features have profoundly influenced its history, its agricultural practices, and its population distribution.
- The Zagros Mountains: This imposing mountain range stretches across western Iran, creating a natural barrier between the Iranian Plateau and the Mesopotamian lowlands. The Zagros are home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna, and their rugged terrain has historically provided refuge for various ethnic groups.
- The Alborz Mountains: Running along the northern edge of Iran, the Alborz Mountains are home to Mount Damavand, the highest peak in the Middle East. These mountains are also a crucial source of water for the country, feeding numerous rivers and providing essential irrigation for agriculture.
- The Iranian Plateau: This vast, arid plateau encompasses much of central and eastern Iran. Its harsh climate and limited water resources have posed significant challenges for agriculture and human settlement. However, the plateau is rich in mineral resources, particularly oil and natural gas.
- The Caspian Sea: The largest enclosed inland body of water in the world, the Caspian Sea lies to the north of Iran. Its shores are home to a diverse ecosystem and provide access to important trade routes.
- The Persian Gulf: A strategically vital waterway, the Persian Gulf borders Iran to the south. Its oil reserves are a major source of wealth for the country, but the Gulf also harbors political tensions and economic rivalries.
The Surrounding Nations: A Mosaic of Cultures and Landscapes
Iran’s geographic position places it at the crossroads of several major civilizations. Its immediate neighbors include:
- Turkey: To the west, Turkey shares a long border with Iran. The two countries have a complex historical relationship, marked by periods of conflict and cooperation. Turkey’s strategic location, spanning both Europe and Asia, makes it a significant player in regional geopolitics.
- Iraq: Situated to the west of Iran, Iraq shares a long and contentious border. The two countries have been embroiled in various conflicts over the centuries, including the Iran-Iraq War of the 1980s. Iraq’s oil wealth and its strategic location have made it a focal point of regional power struggles.
- Afghanistan: To the east, Afghanistan shares a mountainous border with Iran. Both countries have experienced political instability and conflict in recent decades. Afghanistan’s strategic location, bordering several countries, makes it a vital route for trade and transportation.
- Pakistan: Located to the southeast, Pakistan shares a long and complex border with Iran. The two countries have historically enjoyed close ties, but their relationship has been strained by issues of religious extremism and political instability. Pakistan’s nuclear capabilities add another layer of complexity to the regional dynamic.
- Turkmenistan: To the northeast, Turkmenistan shares a relatively short border with Iran. The two countries have been collaborating on energy projects, particularly in the gas sector. Turkmenistan’s rich natural resources, including its vast reserves of natural gas, make it a key player in the Central Asian energy market.
- Azerbaijan: To the northwest, Azerbaijan shares a border with Iran. The two countries have historically maintained close cultural and linguistic ties, but their relationship has been strained by the unresolved conflict over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Azerbaijan’s strategic location, bordering Russia, Turkey, and Iran, makes it a crucial player in the Caucasus region.
- Armenia: Located to the northwest, Armenia shares a border with Iran. The two countries have maintained friendly relations, with Armenia relying on Iran for access to international markets. Armenia’s history of conflict with neighboring Azerbaijan adds another dimension to the regional dynamic.
The Geopolitical Significance of the Region
The map of Iran and its surrounding countries reveals a region of immense geopolitical significance. The region is home to vast energy reserves, crucial trade routes, and diverse ethnic groups. Its strategic location, bridging the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Caucasus, has made it a focal point for international powers seeking influence and resources.
- Energy Resources: The region is rich in oil and natural gas reserves, making it a vital source of energy for global markets. Iran, Iraq, and Turkmenistan are major energy producers, while countries like Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan hold significant reserves. The control and distribution of these resources have been a major driver of regional conflict and international competition.
- Trade Routes: The region sits on important trade routes connecting East and West. The Silk Road, a historic trade route linking China to Europe, traversed through parts of Iran and its surrounding countries. Today, modern transportation routes, including pipelines and shipping lanes, continue to connect the region to global markets.
- Ethnic Diversity: The region is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, each with its own unique culture, language, and traditions. The interaction and interplay of these diverse cultures have enriched the region’s history and shaped its political landscape.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The region has been a site of ongoing geopolitical tensions, driven by factors such as ethnic conflicts, religious differences, and international power struggles. The presence of major military powers, including Russia, the United States, and China, adds another layer of complexity to the regional dynamic.
FAQs by Map of Iran and Surrounding Countries
1. What is the significance of Iran’s location?
Iran’s location at the crossroads of Asia, the Middle East, and Europe makes it a strategically important country. It controls access to major energy resources, trade routes, and cultural centers.
2. What are the major geographic features of Iran?
Iran is characterized by its mountainous terrain, dominated by the Zagros and Alborz ranges, and its vast deserts and fertile plains. The Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf also play significant roles in its geography and economy.
3. What are the main cultural and linguistic groups in the region?
The region is home to a diverse range of ethnic and linguistic groups, including Persians, Kurds, Turks, Arabs, and many others. This diversity reflects the historical interactions and migrations that have shaped the region’s cultural landscape.
4. What are the major geopolitical challenges facing the region?
The region faces numerous geopolitical challenges, including ethnic conflicts, religious tensions, international power struggles, and the control of energy resources.
5. How does the region’s geography impact its economy?
The region’s geography has a profound impact on its economy, influencing its agriculture, energy production, trade routes, and tourism potential.
Tips by Map of Iran and Surrounding Countries
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map of Iran and its surrounding countries will provide a visual understanding of the region’s geography and its political boundaries.
- Research the history and culture of the region: Understanding the history and culture of the region will provide context for its current political and economic situation.
- Explore the region’s diverse ethnic groups: Learn about the different ethnic groups that inhabit the region and their unique cultures and traditions.
- Investigate the geopolitical dynamics of the region: Examine the power struggles, international relations, and conflicts that shape the region’s political landscape.
- Consider the impact of climate change: Climate change is a major factor impacting the region’s environment and its economic development.
Conclusion by Map of Iran and Surrounding Countries
The map of Iran and its surrounding countries reveals a complex and dynamic region with a rich history, diverse cultures, and significant geopolitical importance. Its strategic location, its vast energy resources, and its diverse ethnic groups have made it a focal point for international attention and competition. Understanding the region’s geography, history, and culture is essential for navigating the complexities of this vital part of the world.
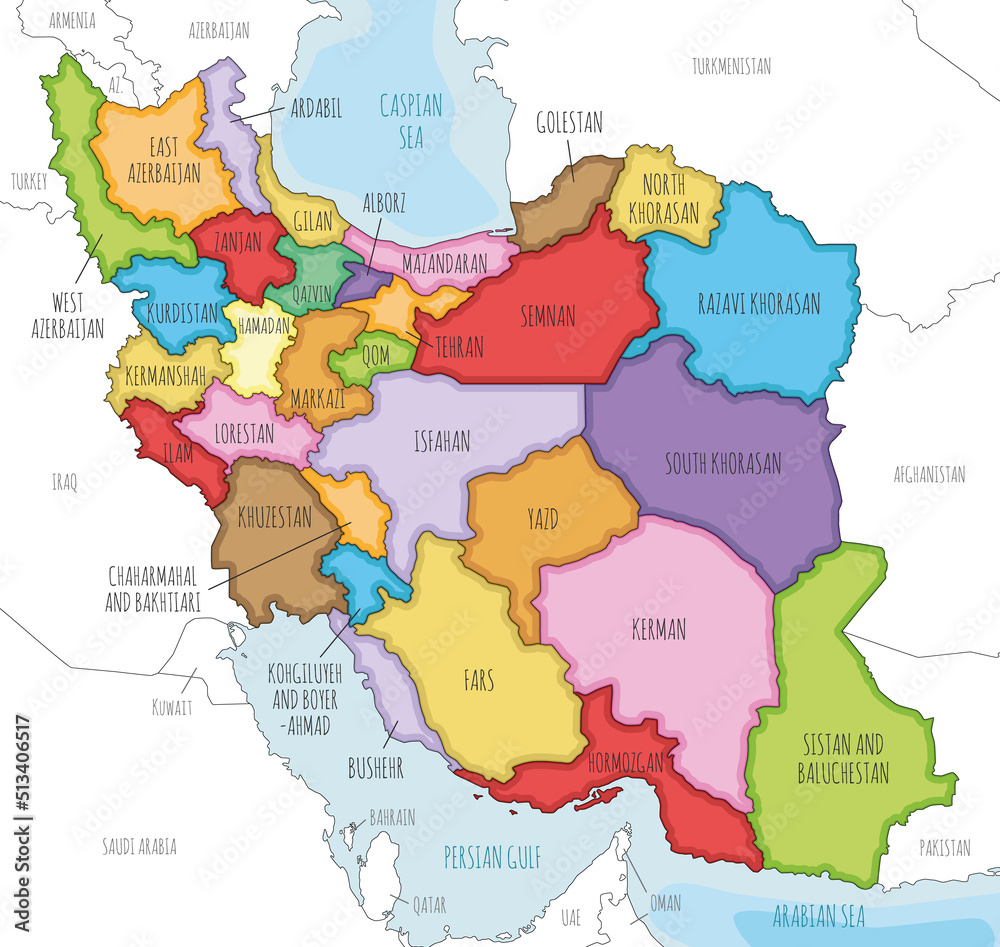



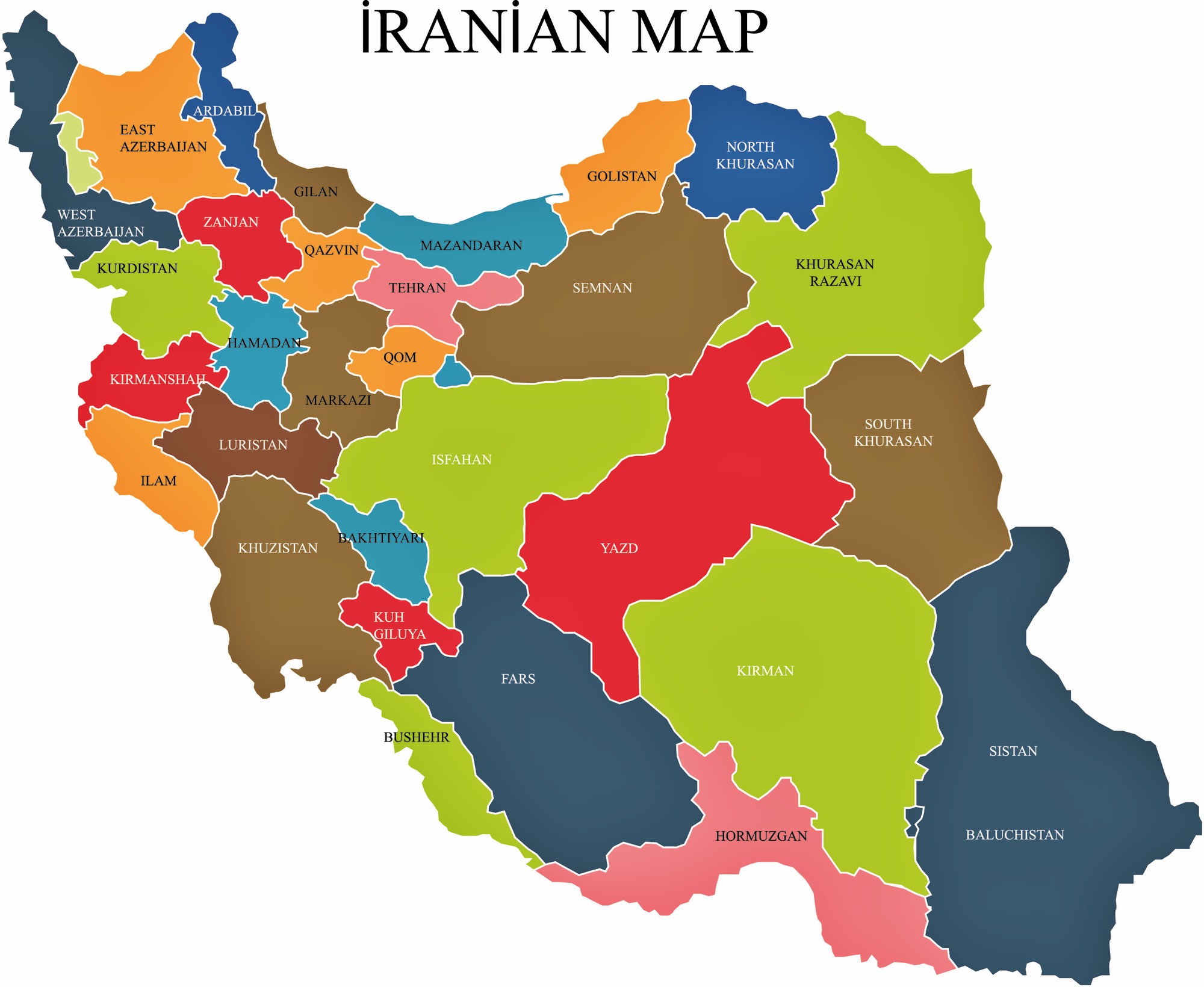


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Iran and Its Neighbors. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!